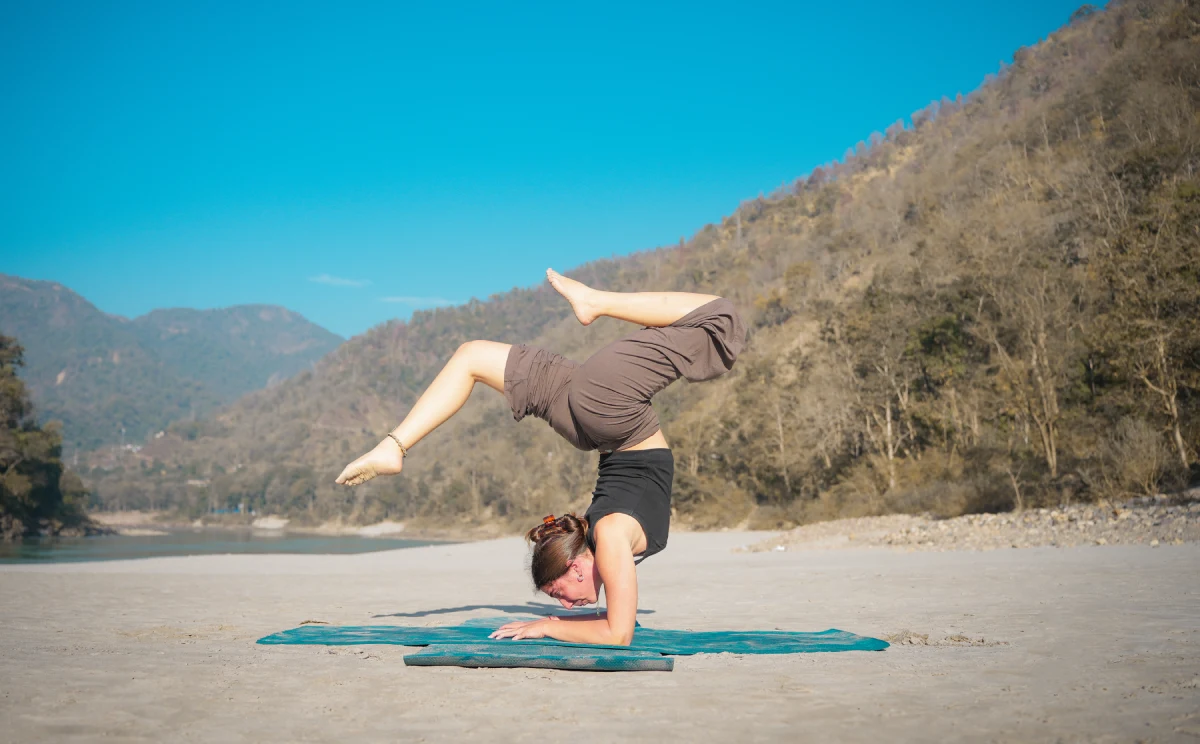
Ashtanga Yoga
Ashtanga is a dynamic version of hatha yoga. It is a six-level
yoga style with a proper series of postures. More than a teaching
session conducted by yog gurus, Ashtanga Yoga is a self-assisted
and practice class. All students are doing the same sequence and
postures, supported by experienced teachers.
Standing Postures
- Samasthiti
-
Sun salutation A & B (Surya Namaskar Series A & B)
- Padangushtasana (Big toes Posture)
- Pada hastasana (Hand under foot posture)
- Utthita Trikonasana (Triangle posture)
- Parivritta Trikonasana (Revolved Triangle Pose)
- Utthita Parshvakonasana (Extended Side Angle Pose)
- Parivritta Parshvakonasana (The Revolved Side Angle Pose)
-
Prasarita Padottanasana (A, B, C & D) (Wide-legged Forward
Fold A, B, C & D)
- Parshvottanasana (Side Stretch Pose)
Intermediate Postures
- Pasasana (Noose Pose)
- Krounchasana (Heron Pose)
- Shalabhasana A, B (Locus Pose A, B)
- Bhekasana (Frog Pose)
- Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)
- Parsvadhanurasana (Side Bow Pose)
- Ustrasana (Camel Pose)
- Laghu Vajrasana (Small Thunderbolt Pose)
- Kapotasana (Pigeon Pose)
- Supta Vajrasana (Reclined Thunderbolt Pose)
- Bakasana (Crane Pose)
- Bharadvajasana (Seated Spinal Twist Pose)
- Ardha Matsyendraasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Pose)
-
Ekapada Sirsasana A, B, C (Seated foot-behind-the-head Pose)
- Dwipada Sirsasana B (Feet behind the head pose)
- Yoga Nidrasana (Yogic Sleep Pose)
- Tittibhasana A, B, C (Firefly Pose A, B, C)
- Pincha Mayurasana (Peacock Feather Stand)
- Karandavasana (Himalayana Duck)
- Mayurasana (Peacock Pose)
- Nakrasana (Crocodile Pose Variation)
- Vatayanasana (Horse Pose)
- Parighasana (Gate Pose)
- Gomukhasana A, B, C (Cow Face Pose)
-
Supta Urdhvapada Vajrasana A, B (Reclining Thunderbolt Pose One
Foot Upward A, B)
-
Mukta Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C (Free Hands Headstand Pose A, B,
C)
-
Baddha Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C, D (Bound Hands Headstand Pose A,
B, C, D)
- Urdhva Dhanurasana (Upward-facing bow Pose)
- Paschimottanasana (West Stretching Pose)
Finishing Postures
- Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported all limbs Pose)
- Halasana (Plow Pose)
- Karnapidasana (Ear-pressure Pose)
- Urdhva Padmasana (Upward Lotus Pose)
- Pindasana (Embryo Pose In Shoulder Stand)
- Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
- Uttana Padasana (Raised Leg Pose)
- Shirshasana (Headstand Pose)
- Baddha Padmasana (Bound Lotus Pose)
- Yoga Mudra
- Padmasana (Lotus Pose)
- Uth Pluthi or Tolasana (Sprung Up)
- Shavasana (Corpse Pose)
Ayurveda
Ayurveda is the oldest and the most natural system of medicine
that originated in India years ago. It is approximately 3000 years
ago medicinal science. Ayurveda is derived from two words, "Ayur"
means "Life" and "Veda" means "Science", thus Ayurveda describes
the meaning "Science of Life" or 'Knowledge of Life'. As per
Ayurvedic Science, the body is made up of five elements, i.e.
Akash (Ether), Vayu (Air), Agni (Fire), Apas (Water), and Prithvi
(Earth). These 5 elements create 3 doshas namely, Kapha, Vata and
Pitta. When these are balanced, then an individual remains healthy
and when these are imbalances, an individual remains ill. Ayurveda
helps in balancing all of these to give you a healthy lifestyle.
The 300 Hours Yoga Course explains,
- What is Ayurveda?
- Fundamentals of Ayurveda
- Tridosha (Vata, Pitta and Kapha)
- Prakriti (Know Your Constitution)
-
Pancha Mahabhuta [Earth (Prithvi), Water (Jal), Fire (Agni), Air
(Vayu) and Aether / Space (Aakash)]
- Vikurti (After Creation)
-
Sapta Dhatu or 7 Body Elements (Rasa, Rakta, Mamsa, Meda, Asthi,
Majja and Sukhra)
- Mala (Waste Products)
- Srotas (Body Channels) - 16 as per Ayurveda
- Agni (Digestive Fire)
- Koshta (Alimentary Tract)
- Ama (Undigested Metabolic Toxins)
Bandhas (Energy Locks)
Bandhas is the Sanskrit word which means Lock. The aim of it is to
block the energy flow from a particular part of the body. When the
lock is opened, then the energy flows properly throughout the body
and maintains overall wellness and vitality.
What'll you learn?
- Meaning and Importance of Energy Lock
- Kundalini Awakening
- Bandhas and Prana
- Unblocking the system for energy flow through Bandhax
-
3 Energy Knots (Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva) and How to Open Them
- The outcome of Bandhas practice
- Precautions
- Health and Spiritual Benefits
Practices (Beginners and Intermediate Level)
- Agnisar - Advance Level (Preparation to Uddiyana)
- Advance Level Vahir Kumbhaka (External Retention)
- Advance Level Antar Kumbhaka (Internal Retention)
- Ashwini Mudra to prepare Mulabandha
- Vajroli Mudra to prepare Mulabandha
- Mula bandhas (Anal lock)
- Uddiyana bandha (Abdominal lock)
- Jalandhar Bandha (Throat Lock)
- Maha Bandha (Great Lock)
Ganga Beach Sadhna
The ghats near the Ganges are tranquil with the aesthetic scenery,
soothing views and sheer beauty. You can feel true peace by just
sitting near the Ganga. To bring a soothing experience to the
course, every Thursday morning at our school is scheduled for the
yoga sadhanas on the banks of the holy river, Ganga.
The lessons:-
- Asana
- Pranayama
- Meditation
- Ganga Puja
Hatha Yoga
Hatha Yoga sessions conducted by our school are a positive workout
for one's physical and mental wellness. It originated years ago
with the aim to attain health and peace. The practice also
benefits you with strength and flexibility.
Hatha Yoga works on the basic aim of,
- Promoting health and longevity
- Strengthening the mind
- Awakening the Kundalini
Practices:
- Joints and glands exercise foundation practices
- Joints and glands exercise advanced practices
- Centering postures series (Yoga Sequence Builder)
- Surya Namaskar (Sun Salutation)
- Chandra Namaskar (Moon Salutation)
- Standing postures series
- Kneeling postures series
- Sitting Postures series
- Forward bending postures series
- Backward bending postures series
- Supine postures series
- Prone Postures series
- Fire Series series
- Inversions series
- Twisting postures series
- Balancing Postures series
- Relaxing Posture series
- Meditative Asana Series
Philosophy Of Hatha Yoga
You have done practice sessions but what about theory? It is also
as important as practice sessions. If you are not theoretically
aware of Hatha yoga and its elements, you are not able to practice
it well.
- Surya Namaskar Philosophy
- Hatha Yoga Philosophy
- Kundalini Awakening
- Asanas
- Yog Sadhana
- Benefits of Hatha Yoga Asanas
- Rules and Regulations
- Advancing Yoga Poses
Mantra & Mantra Diksha
Mantra
Mantras are sacred sounds, words, or phrases which are recited to
attain spiritual attention. In other words, a mantra is a tool of
the mind. It helps the mind in focusing better.
Sanskrit syllable
- 58 syllables
- Power of vibration of all syllables
- Mantra vibration in chakras
Healing mantras
- Mantras for physical healing
- Mantras for mental healing
- Mantras for emotional healing
- Mantras for spiritual healing
Mantras for planetary disorders
- Mantra for sun
- Mantra for moon
- Mantra for Saturn
- Mantra for vrihaspti/guru
- Mantra for Mangala
Mantra for healing the different diseases
- Mantra for Cancer
- Mantra for HBP
- Mantra for heart problem
- Mantra in pregnancy
- Mantra for stress relief
- Mantra for concentration
Mantra Healing for all planets
- Surya Mantra (Sun Mantra) -Om Hring Hraung Suryay Namah
- Chandra Mantra (Moon Mantra) - Om Aing Kling Somay Namah
- Mangala Mantra - Om Hung Shring Bhaumay Namah
- Buddha Mantra - Om Aing Shring Shring Budhay Namah
-
Brihaspati Guru Mantra - Om Hring Cling hung Brihsptye Namah
- Shukra Mantra - Om Hring Shring Shukray Namah
- Shani Mantra - Om Aing Hring Shring Shanaishchray Namah
- Rahu Mantra - Om Aing Hring Rahave Namah
- Ketu mantra - Om Hring Aing Ketave Namah
Mantra Diksha
Mantra Diksha is an important initiation ceremony of the tradition
that is scheduled to be done on the first day of the course. After
getting ready, students are advised to dress up in white to join
the opening ceremony of the yoga course. The ceremony is conducted
by respected Pandit Ji or Guru Ji who transmits energy inside you
with powerful mantras.
What'll happen during Mantra Diksha?
- Dhara Pujan (Worship to mother earth)
- Ganesh Pujan (Worship to Ganesha to remove obstacles)
- Hawan (Fire ceremony)
- Aarti (Prayer)
- Music
- Kirtan
- Gayatri diksha
- Guru Mantra
- Distribution of books and teaching materials
Chakras
Chakras are energy points of the body. They are believed to be
spinning disks which is needed to be open and aligned for healthy
well-being. In the human body, there are 7 chakras.
Characteristics of each chakra,
Muladhara Chakra or Root Chakra
- Sound: Lam
-
Location: Between the anus and genitals, the
base of the spine
- Petal: Four Petals
- Color: Red
Swadhistana or Sacral Chakra
- Sound: Vam
- Location: Below the bellybutton
- Petal: Six Petals
- Color: Orange
Manipura or Solar Plexus Chakra
- Sound: Ram
- Location: The Upper Abdomen
- Petal: Ten Petals
- Color: Yellow
Anahata or Heart Chakra
- Sound: Yam
- Location: Above the heart
- Petal: Twelve Petals
- Color: Green/Pink
Visuddha or Throat Chakra
- Sound: Ham
- Location: Throat
- Petal: Sixteen Petals
- Color: Blue
Ajna or Third Eye Chakra
- Sound: Om
- Location: Between the eyebrows
- Petal: Two Petals
- Color: Indigo
Sahasrara or Crown Chakra
- Sound: Silence
- Location: Top of the head
- Petal: One Thousand Petals
- Color: Violet, Gold, White
Meditation (Dhyana)
Just like you involve your body in physical exercise for its
benefits, in the same way, meditation is an exercise for mental
health. With the power of meditation, you can control your mind
and block negative and unnecessary thoughts. You enter into a deep
state of relaxation where peace is the ultimate goal.
During the meditation class, you are advised to sit quietly by
keeping your focus on a single thing. It helps you in eliminating
tension and stress. With the 300 Hours yoga teacher training
course, you get to learn basic and intermediate techniques of
meditation. The four weeks program work as,
Week 1: Introducing Meditation and Building
Foundation
Week 2: Making the mind able to focus on a single
aspect with concentration process and exercises.
Week 3: Meditation Techniques
Week 4: Chakra Awareness and Kundalini Meditation
What'll you learn?
- Mind and its role in meditation
- Nature of mind
- Why the mind is anxious?
- Meditation as Reverse Journey of Pratiprasava
- Brain Waves
- Music and Meditation
- Emotional Purification Meditation
- Past Life Healing with Meditation
- Samadhi with Meditation
Styles Of Meditation Practices
Himalayan Meditation Practices
- Advance Foundational Meditation Practice
- Breath- Mind- Mantra Awareness
- Trataka Meditation
- Anapana Meditation
Nada Meditation Practices
- Music Meditation
- Pranava Meditation
- Advance Mantra Meditation
Active Meditation Practices
- Dynamic Moving Meditation (Osho)
- Contemplative walking
- Meditation in daily life
Tantra & Kundalini Meditation Practices
- Meditation for Muladhara Chakra
- Meditation for Swadhisthana Chakra
- Meditation for Manipura Chakra
- Meditation for Anahata Chakra
- Meditation for Visuddhi Chakra
- Meditation for Ajna Chakra
- Meditation for Sahasrara Chakra
- Guru chakra Meditation
- Kundalini Meditation
Vipassana & Passive Meditation Practices
- Breath Awareness
- Mindfulness and Sensation
- Total Awareness Practice
Kirtan Dhyan
Mantra Japa
Silence Practice
Mudras
Mudra is a symbolic gesture. It is normally practiced with hands
and fingers, explaining the flow of energy in the subtle body. It
brings a wondrous change in body and mind.
The 300 Hours Yoga Course explains,
Hasta Mudra (Hand Mudra)
- Yoni mudra
- Linga Mudra
- Bhairava Mudra
- Bhairavi Mudra
- Energy Mudra
- Viparita Karnai Mudra
- Mahabandha Mudra
- Mahabheda Mudra
Kundalini Mudra
- Ashwini Mudra
- Vajroli Mudra
- Sahajoli Mudra
Shambhavi Mudra
Pranayama (Breathing Practices)
Prana, the life energy Yama means control. It is the foundation
practice of the traditional form of yoga. It is not just a
breathing practice but much more than this. The class of pranayama
reveals its secrets and the power of pranayama to gain the right
health, peace, and balance.
Four Weeks of Pranayama
- Week 1: Advanced pranayama practices
- Week 2: Variations and experiments
- Week 3: Awakening nadis and chakras
-
Week 4: Teaching practices and mastery of
breathing
Topics:
- What is Pranayama?
- How pranayama brought happiness
- Physiology of prana
- Elements in nature of prana
- Prana body types
- Astrology of Breathing science
- Prana and it routes
- How prana flows in the body
- Prana & Consciousness
- Number of breaths we take
- Research on prana
- Health parameter with breath length
- Guideline and discipline of pranayama
Intermediate and Advance Practices of Pranayama
- Clavicular Pranayama (Upper Chest Pranayama)
- Thoracic Pranayama (Middle Chest Pranayama)
- Koshtiya (Diaphragmatic Pranayama)
- Full body Yogic Pranayama
- Pranava Pranayama (Om Meditation Breathing)
- Nadi Shodhana Pranayama or Anulom Vilom Pranayama
- Bhastrika Pranayama (Bellows Breath)
- Kapalbhati Pranayama (Skull Shining Breath)
- Bhramari Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath)
- Ujjayi Pranayama (Ocean Breath)
- Sitali Pranayama (Cooling Breath)
- Sitkari Pranayama (Hissing Breath)
- Murcha Pranayama (Swooning Breath Yoga)
- Surya Bhedi Pranayama (Right Nostril Breathing)
- Chandra Bhedi Pranayama (Left Nostril Breathing)
Anatomy & Physiology (Sharir Vigyan)
In yoga, anatomy is a crucial subject for yoga teachers and
learners. In the class, you will get to know physical anatomy and
spiritual anatomy.
Physical Anatomy
- Prana supply to the respiratory system
- Function of cells
- Digestive system
- Circulatory system
- Endocrine system
- Physical transformation with yoga
- Hormone secretion in yoga
- Effects of pranayama on the respiratory system
-
Effects of Yoga practice and Nauli on the digestive system
- A muscular and skeletal system with advanced postures
- Therapeutic applications of Yoga postures
- Avoid injuries in asana class
- Anatomy of pelvic griddle and spine
Spiritual Anatomy
- Advanced details regarding the energy channel
-
Anatomy of the 7 chakras (Muladhara Chakra, Swadhisthana Chakra,
Manipura Chakra, Anahata Chakra, Visuddhi Chakra, Ajna Chakra,
Sahasrara Chakra)
- Kundalini (Prime Energy and Souce of All Creativity)
- Pancha Kosha (5 Layers)
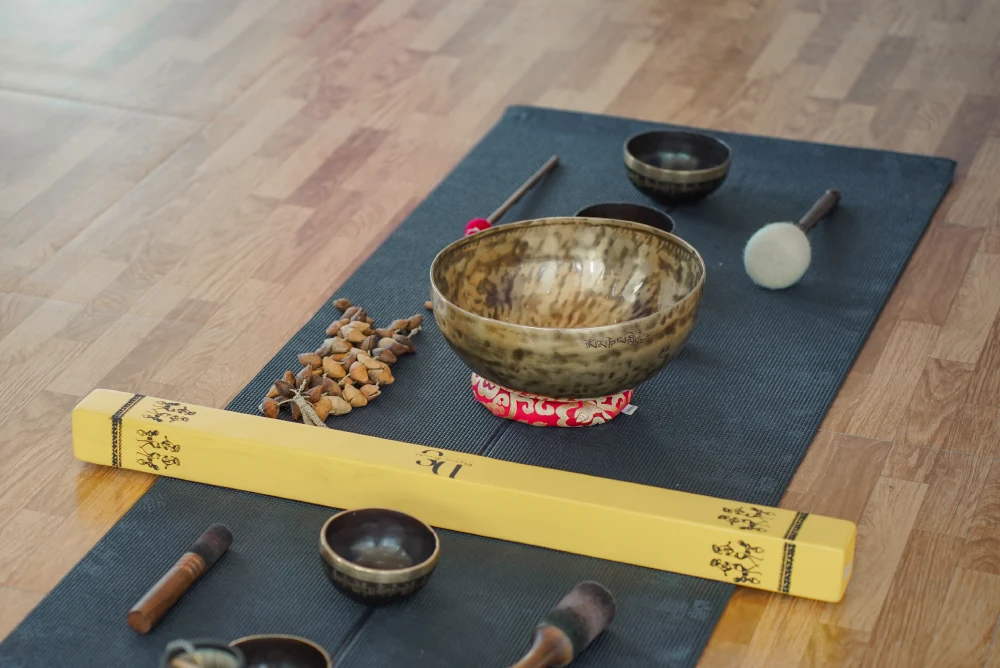
Yoga Kriya & Cleaning (Shatkarma)
"Shat" means "Six" and "Karma" means "Actions". Thus, as per yogic
science, Shatkarma is six cleansing actions that help to clean
your body and mind. It is well described in the Hatha Yoga
Tradition. Shatkarma is an important practice to maintain a
balance between body and mind and also promote well-being. The
practice eliminates toxins from the body and unblocks energy
channels.
With the 300 Hours Yoga TTC, you will learn,
- 11 major systems of the body
- Body purification
- What is Shatkarma or Shatkriya?
- Ancient scriptures of Hatha Yoga Pradipika
- Gheranda Samhita
- Precautions while performing shatkarmas
Practices
- Vamana Kriya (Purification of the upper digestive tract)
- Vastra Dhauti (Cleansing of the stomach and oesophagus)
-
Laghu Sankha Prakyalana (Cleasning of the stomach and
intestines)
- Bama Nauli Kriya
- Dakshina Nauli Kriya (Cleansing of the right abdomen)
- Vyaghra Kriya
Yoga Nidra (Psychic Sleep)
Yoga Nidra is also known as Psychic Sleep. The practice creates a
state between waking and sleeping. It is a state of consciousness.
One can go into this deep and conscious sleep with the practice of
guided meditation. Yoga Nidra can also be termed as the victory
over sleep. You can relax your mind and complete the sleep of 8
hours in just a short practice of yoga nidra. When you go through
the epic, Mahabharata, you get to know that Arjuna (one of the
Pandavas) was associated with Yoga Nidra.
Week Wise topics of the 300 Hours Yoga TTC,
-
Week 1: Antar Mauna Yoga Nidra (Inner Silence)
-
Week 2: Yoga Nidra with 61 points blue star
- Week 3: Subtle body and Yoga Nidra
- Week 4: Chakra awareness with Yoga Nidra
What'll you learn?
- Sleep Awareness
- Subtle Body
- From the state of consciousness to superconscious
- Therapy of Yoga Nidra
- Yoga Nidra as a healing practice
- Why is sleep called Yoga here?
- New patterns of habits
- Personality transformation with Yoga Nidra
- Language and Yoga Nidra
Yoga Philosophy (Yoga Darshana)
Yoga Philosophy is a powerful subject that can change one's life.
Many are confused that it only exists in Patanjali's Yoga Sutras
but this is not true. It is the philosophy of life which can also
be found in Bhagwat Geeta, Hatha Yoga Pradipika and Upanishads.
The basic and main philosophy of yoga is simple, body, mind, and
soul are one and one can not separate them.
During the 4 weeks of the 300 Hours Yoga Course, Yoga Philosophy
will explain to you the motive of life.
Week 1: The World of Enlightenment (Yoga Samadhi)
- Yoga and Yoga Samadhi
- How to achieve Samadhi?
- Discipline of Yoga
- States of mind
- Controlling the mind
- What is Samadhi?
- What if we are not in the state of Samadhi?
-
The right knowledge, wrong knowledge, imagination, sleep &
memory
- Why practice Yoga Samadhi?
- Self-practice
- Types of Samadhi
- Yogi who born with yoga and bodiless yogi
- How to achieve Samadhi?
- What is God?
- What is Om?
- How to overcome obstacles in yoga?
- The utmost Samadhi
Week 2: (Yoga Sadhana)
- Tapasya (Intense practice of Yoga)
- How to practice Tapasya?
- Swadhyaya (Self-Analysis, self-discovery)
- Surrender to the Divine
- Kriya Yoga?
- Ignorance and emotional attachment
- Minimising pain
- Past life; pain and pleasure
- How pain lives with you and how it generates and vanishes
- Clear perception
- Right action
- Stability
- Control of sense organ
- Experience of self
- Source of liberation
-
How to achieve total withdrawal and separation of mundane
psychology
- Viveka kyati – insight discrimination
- Eight limbs of yoga
Week 3: Yoga Vibhuti
- Concentration
- Meditation
- Samadhi
- External and internal yoga
- How can a yogi know the past and future
- Understanding the language of animals
- Know about the past life
- Making the body invisible
- How Yogis receive the knowledge of the entire cosmos
- How cessation of hunger and thrust is achieved
- Acquiring complete stillness
- Celestial beings
- How the flash of illumination happens
- How can one have knowledge of the mind
- Siddhis? Are they helpful or hindrances for Sadhana?
- How can one enter another’s body
- How can a Yogi walk on thorns and water
- Achieving the divine sense of hearing
-
How can one make a body as light as cotton wool that can soar in
the sky
-
Achieving glorification and indestructibility of bodily
qualities.
Week 4: Yoga Kaivalya
- How Siddhi generates
- Achieving Kaivalya (liberation)
- Revision of the first week- Samadhi Yoga
- Revision of the second week –Sadhana Yoga
- Revision of the third week –Vibhuti Yoga
- Revision of the fourth week – Kaivalya Yoga
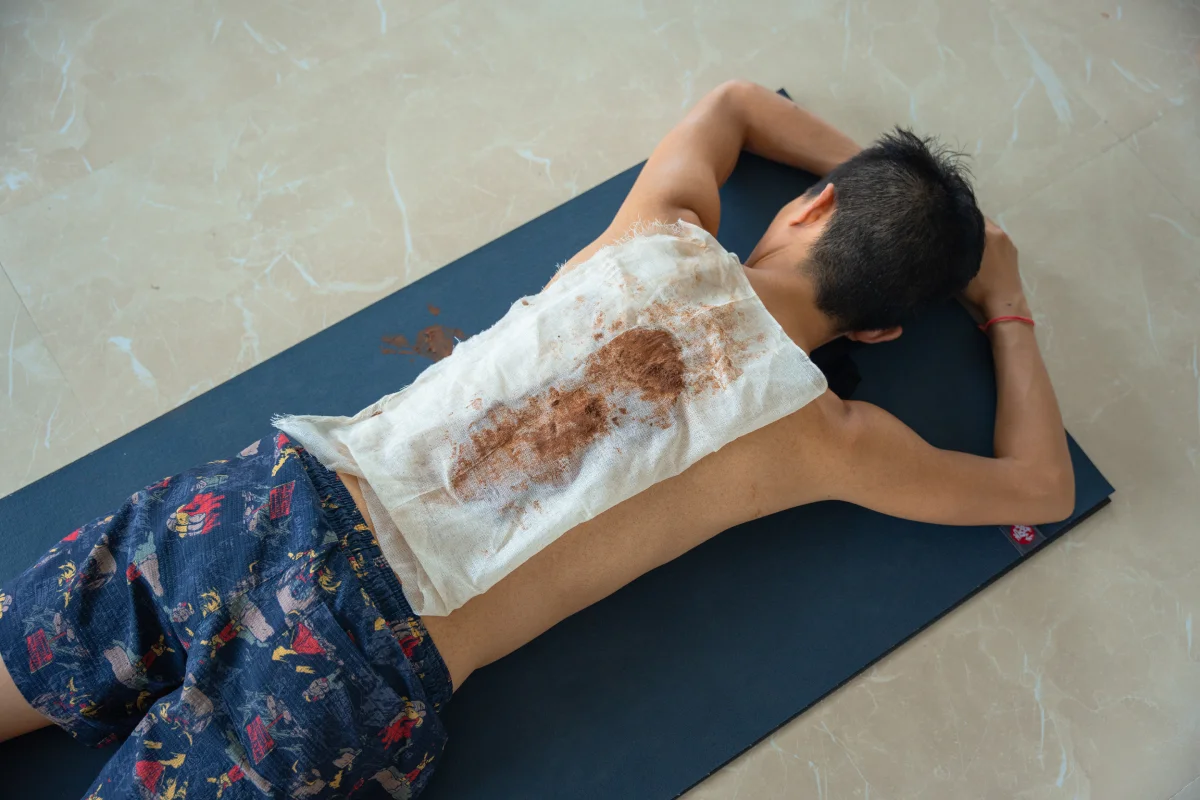
Yoga Therapy
Yoga is the wellness science for nurturing the body, mind and
spirit. It is the natural healing process to keep you healthy and
free from illness. Yoga therapy uses yoga postures, breathing
exercises (pranayama), meditation, and other practices to improve
physical and mental well-being. Yoga therapy encourages the
amalgamation of the body, mind, and spirit.
In the 300 Hours Yoga Course, you will learn,
- The disease of the head and neck
- Headache
- Thyroid
- Heart problems
- Circulatory problems
- Respiratory system and its disorders
- The common cold
- Bronchitis and Eosinophilia
- Asthma
- Sinusitis and Hay Fever
- Tonsillitis
- Disorder of the Digestive system
- Upper Digestive disorders
- Peptic Ulcer
- Constipation
- Colitis
- Acute Gastro Enteritis
- Diabetes
- Hepatitis
- The problem of Obesity
- Arthritis
- Cervical Spondylitis
- Back pain
- Slipped Disk and Sciatica
- Kidney stones
- Menstrual disorder
- Disorders of the male reproductive system
- Hernia
- Skin problems
Yoga For Health
- Yogic counselling for a healthy life.
- Yogic techniques to use in daily lifestyle.
-
Yoga cures common diseases like Headaches, migraine, colds,
sinus, etc.
-
Yoga tools for back issues like backache, slipped disk,
sciatica, diabetes, thyroid, spinal deformities, obesity, etc.
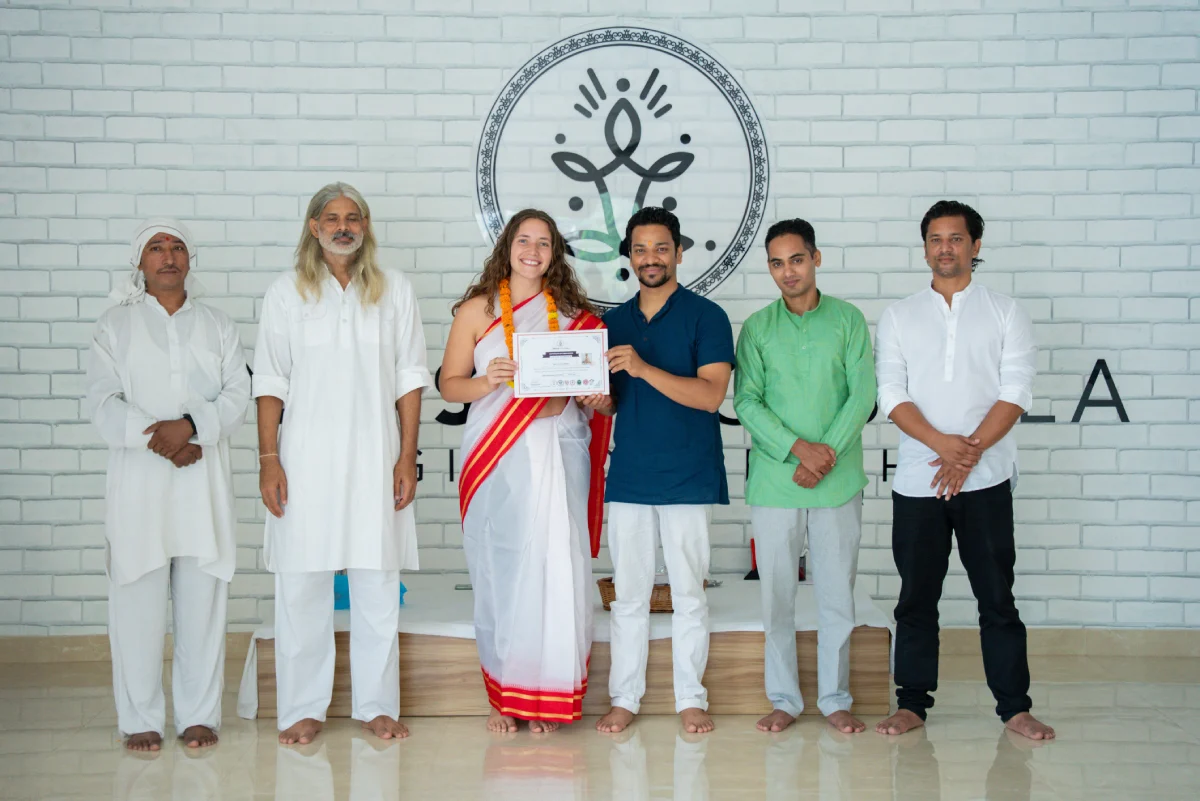
Evaluation & Certification
Yoga is the education of life and if you wish to clear the
advanced yoga program of 300 hours, then do follow the criteria
given below:
-
Get a registered certificate of the 300 hours yoga ttc with a
registered yoga school
- Stay present in all lectures
- Submit assignments timely
- Conduct full yoga sessions
- Achieve passing marks at the end of the course










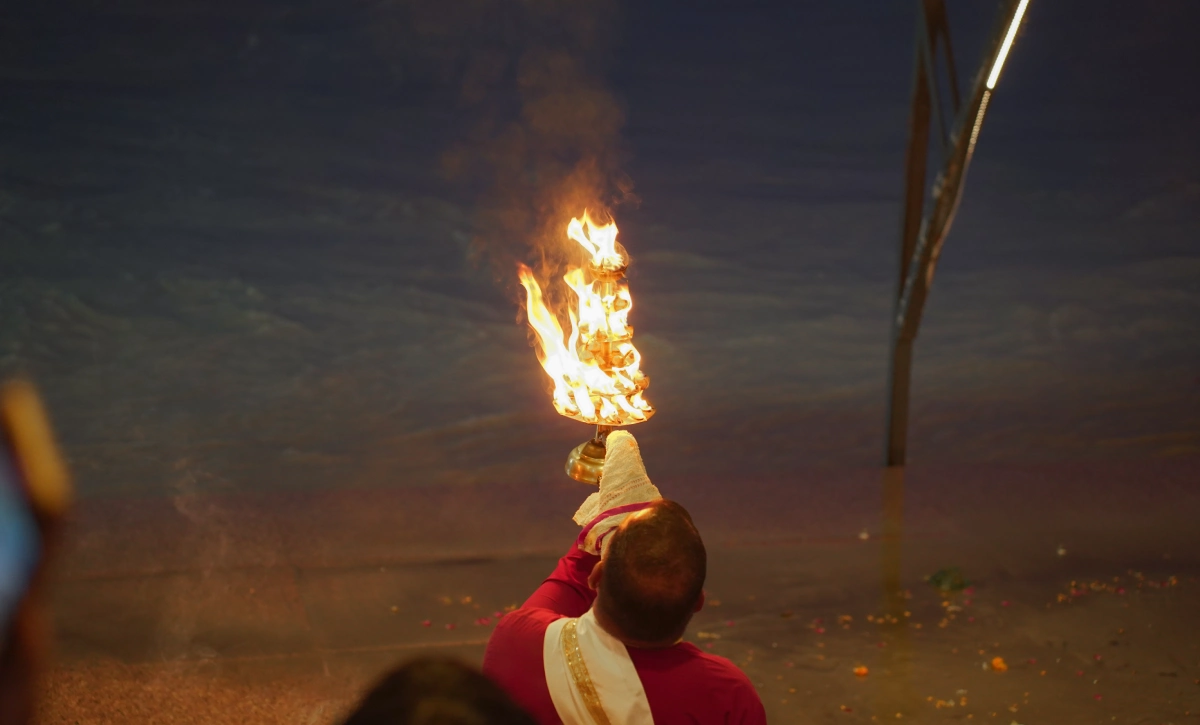


























































































































































































































 Enroll Now
Enroll Now